- This is what happens to your skin when it’s overexposed to the sun:
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Collagen breakdown
This is what happens to your skin when it’s overexposed to the sun:
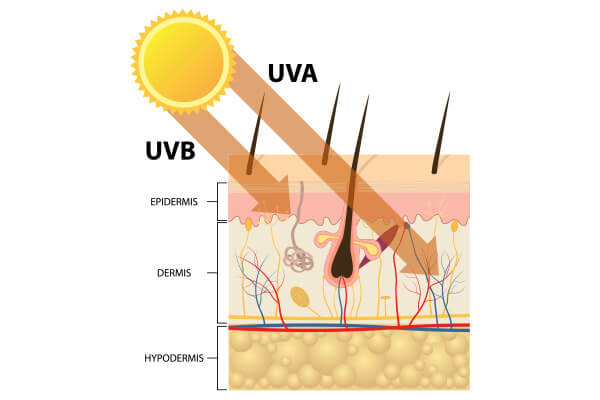
Pigmentation and sunburn
When your skin comes in contact with sunlight, its melanocytes produce melanin to shield it from sun damage. The resulting chemical reaction causes pigmentation that darkens your skin and causes it to tan. Prolonged sun exposure damages the skin cells and can cause hyperpigmentation, which presents itself in the form of dark spots. When you’re exposed to more UV rays than the melanin in your skin can protect you from, you suffer from sunburn, which results in your skin cells dyeing.
Fine lines and wrinkles

Epidermal growth factors heal inflammation, and are vital for healthy skin. They help produce collagen, elastin, and fibroblasts all of which help in skin regeneration. However, ultraviolet radiation can destroy these epidermal growth factors. This results in the formation of fine lines, wrinkles and other signs of premature ageing, as there is a reduction in the production of essential protein in the skin.
Age spots
A freckle is caused when the skin's pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) are damaged, which leads to enlarged blemishes. Larger freckles, also known as age spots, can typically appear on the back of your hands, chest, shoulders, and arms. While age spots are frequently seen in older adults, it’s important to note that they are not age-related, but are in fact, a consequence of sun damage.
Collagen breakdown
UV radiation can cause collagen to break down at an extremely quick pace. It penetrates the dermis (the middle layer of the skin), and causes an abnormal buildup of elastin. These accumulated elastins produce enzymes that weaken over time, and eventually break down the collagen-- a phenomenon called solar elastosis-- and create "solar scars". Continuous exposure to UV rays speeds up the formation of wrinkles, sagging skin and discoloration. It can also cause the walls of blood vessels to become thinner, leading to easy bruising, and spider veining (telangiectasias) on the face.
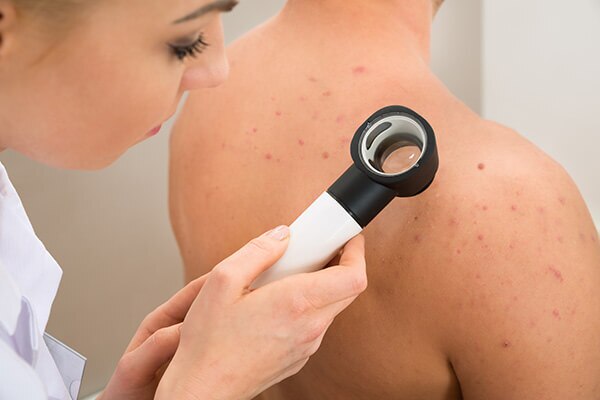
Skin cancer
UV radiation is one of the major creators of free radicals. When the skin experiences inflammation, free radicals begin to form, which multiply very quickly and damage your skin cells along the way. Free radicals not only increase the number of enzymes that break down collagen, but also alter a cell's genetic material in a way that can lead to cancer. The three major types of skin cancer are melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Not all types are fatal, as some of them are curable. The treatment process, however, can be extremely painful and leaves permanent scars on the areas affected by the cancer.
Counteracts anti-aging products
UV damage counteracts the benefits that antioxidants, peptides, ceramides, and other ingredients present in anti-aging products. Hence, it is advised to apply sunscreen with an SPF formula even after you’ve used these anti ageing products.
















 Privacy Notice
Privacy Notice
Written by Priyanka Jaising on 8th Mar 2018